Meta Description only in the rendered HTML
This means that the URL in question has a meta description that is not present in the response HTML of the page, it only appears after JavaScript has executed.
Why is this important?
Google clearly state in their documentation that it is fine to use JavaScript to set or change the meta description:

However, this doesn't mean that this is the optimal way to deliver page content to search engines.
The problem is that rendering webpages is a resource intensive task, and it takes significantly longer than simply grabbing source (response) HTML content.
This is why Google essentially crawl URLs in a two-stage process: their 'first look' is of the HTML response, then they render the page and have a 'second look' at the rendered HTML, then they update the index based on what they found in the rendered HTML.
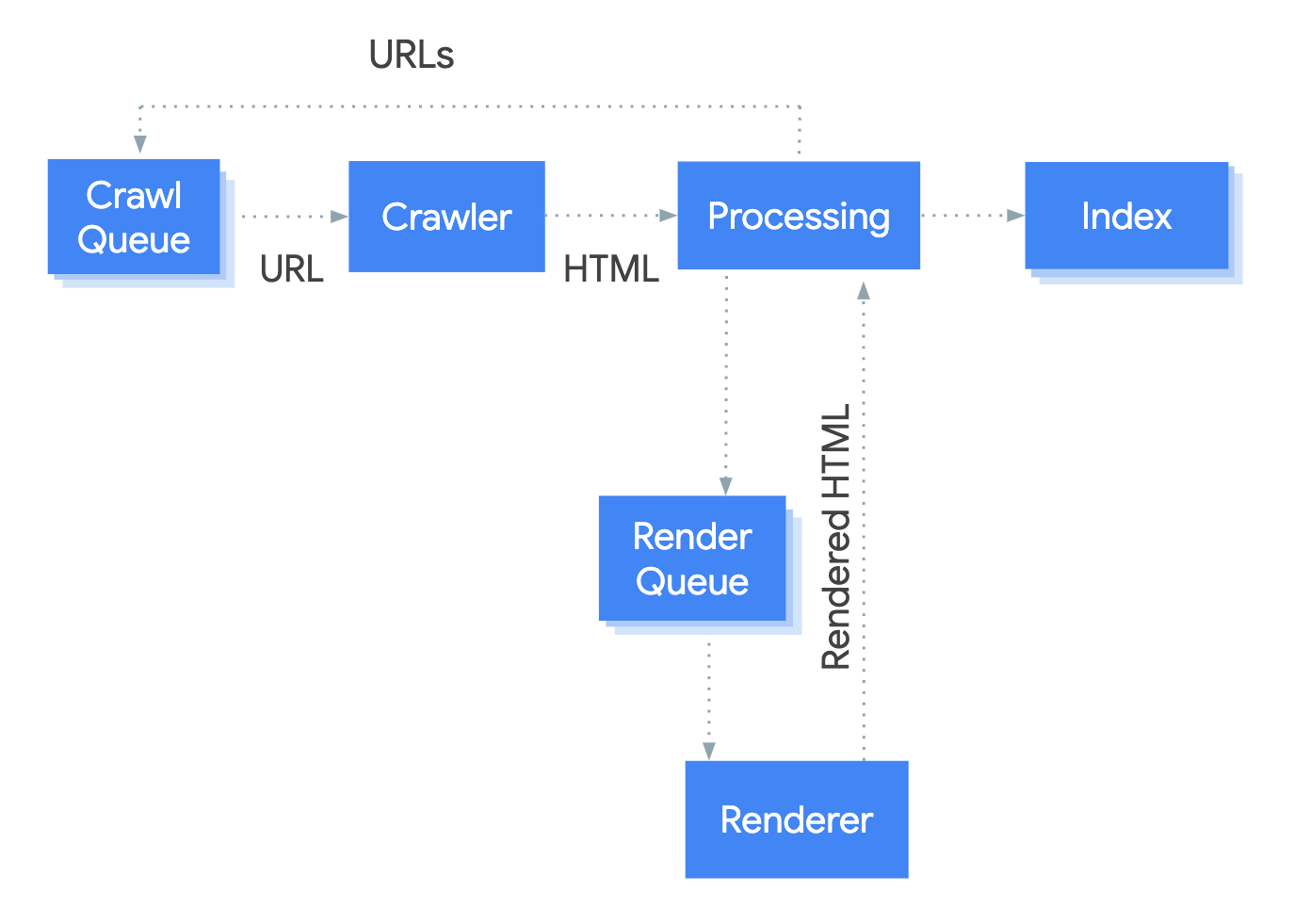
As a result, URLs can and do enter the index initially based on this 'first look' (i.e. the HTML response) and there will be an indeterminate amount of time between this and the 'second look' (i.e. the rendered HTML).
So it is important that the HTML response contains all of the core elements as you want them to be included in the index, including the meta description.
If there is no meta description in the HTML response, then the only way for Google to index the page would be if they were to choose their own meta description. And if lots of the body content is also only available after rendering has occurred, they will have very little to go on when generating their own meta description.
This becomes particularly problematic if the page content (and meta description) is changing all the time, you can easily end up in a situation where Google have the 'old' version indexed.
What does the Hint check?
This Hint will trigger for any internal URL that contains a meta description in the rendered HTML but not in the response HTML.
Examples that trigger this Hint
This Hint will trigger for any URL that has a meta description in the <head> of the rendered HTML, that is not present in the response HTML.
For example, if the response HTML looked like this:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta name="robots" content="index,follow">
...
</head>
<body>...</body>
</html>And the rendered HTML looked like this:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta name="description" content="Visit this amazing page">
<meta name="robots" content="index,follow">
...
</head>
<body>...</body>
</html>How do you resolve this issue?
In general, it is not a good idea to rely on JavaScript for the core on-page elements, otherwise you may find that pages are getting indexed with the wrong data, or taking a lot longer to get indexed. Additionally, Google may not always be able to render pages correctly, or it may not be able to execute JavaScript at all.
The meta description is an important on-page element - you really want to have this available to Google on their first look of the page.
To resolve this issue, you would need to work with the development team to ensure that the meta description is present in the HTML response, and is not then changed by JavaScript during rendering.
Further Reading
 Sitebulb Desktop
Sitebulb Desktop
Find, fix and communicate technical issues with easy visuals, in-depth insights, & prioritized recommendations across 300+ SEO issues.
- Ideal for SEO professionals, consultants & marketing agencies.
 Sitebulb Cloud
Sitebulb Cloud
Get all the capability of Sitebulb Desktop, accessible via your web browser. Crawl at scale without project, crawl credit, or machine limits.
- Perfect for collaboration, remote teams & extreme scale.

