Broken internal URLs
This means that the URL in question was not successfully audited, and had a crawl status of either Not Found, Error, Forbidden or Timeout.
Why is this important
Broken URLs are unwelcome, as they result in a poor user experience - since the user is unable to access the page content - and can also have a negative SEO impact, depending on the type and scale of the issue.
Broken URLs often also give rise to broken links - where other internal URLs contain ongoing links that point at the broken URL - and this is typically a situation that requires a resolution.
What does the Hint check?
This Hint will trigger for any internal URL which does not return a 2XX or 3XX HTTP status.
Examples that trigger this Hint
Consider a URL https://example.com/page1
The Hint will trigger for this URL if it had any of the following:
- HTTP Status code of 4XX
- HTTP Status code of 5XX
- Crawl Status of 'Timeout'
- Crawl Status of 'Error'
How do you resolve this issue?
Depending on the type(s) of broken URLs you are dealing with, you'd need to handle each one differently.
The types of broken URLs are:
- Not Found - this relates to a 404 status code, and is the most unambiguous form of broken link (Note: this also covers the status 410 (Gone)). It simply means that the content is no longer available on the URL in question (effectively, the page has been deleted). 404s are normal, as it is normal for content to be deleted, and typically dealing with 404s means dealing with broken links (see below).
- Error - this can relate to 5XX server errors, or other crawl errors, which meant Sitebulb was unable to access the content. Typically if you encounter errors you will need to spend some time understanding what has caused the error. A site crawler like Sitebulb should not cause server errors, so if you see lots of these you may need to speak to a developer or server admin to investigate this further.
- Forbidden - this relates to a 403 status code, and might happen due to a server configuration issue. If you have been able to crawl most of a site successfully, but certain pages are Forbidden, it may be that the server has started to block requests coming from your IP address.
- Timeout - this means that the page has taken too long to return data, and Sitebulb has given up waiting. Timeouts can be an indication of a poorly configured server, an underpowered server, or pages that are running extremely large or complex database queries.
How to handle broken links
Broken links are most commonly associated with URLs that are 'Not Found', and they mean that there are broken URLs which have incoming links from other pages on the website. In other words, the broken pages are part of the crawlable website architecture.
Broken links are bad for both SEO and user experience, and in order to fix them you need to identify all the pages that link to broken URLs, and update or remove the href attributes that reference any broken URLs.
You can find this data in one of two ways in Sitebulb - either looking at each page one by one, or by looking at all the pages in a bulk export.
Each page one by one
From the URL List, click the blue button URL Details to open up the overlay.
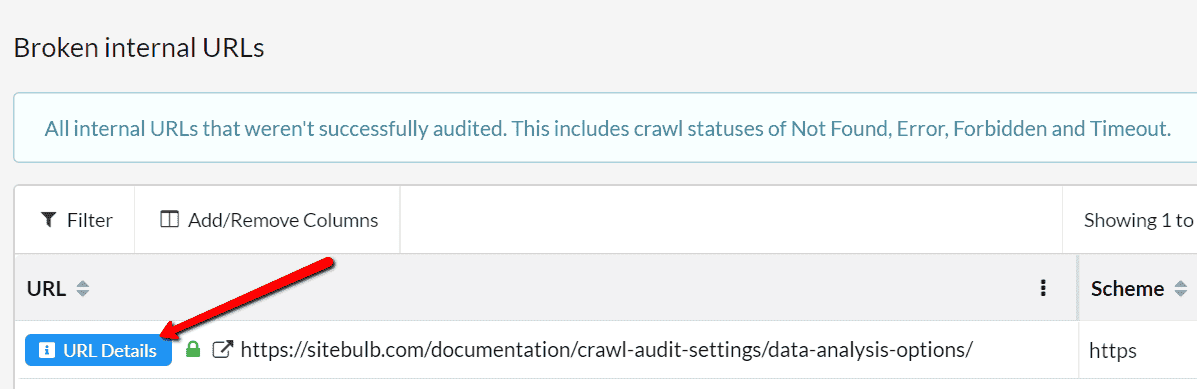
From here, navigate to the tab Incoming Links.
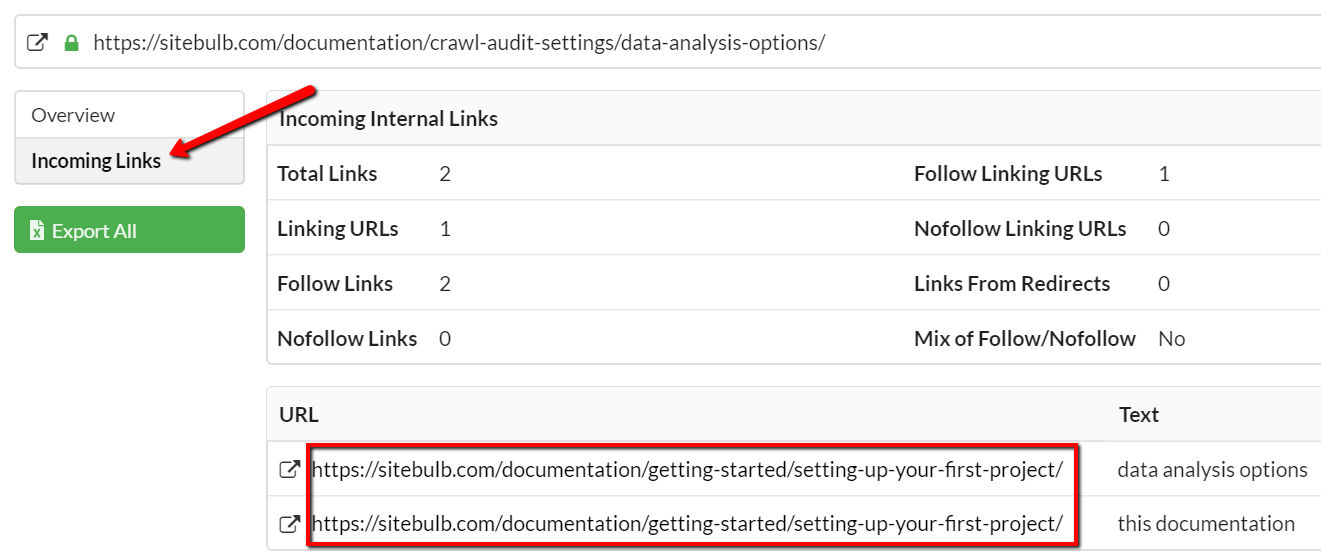
This will show you all the URLs that link to the broken one, along with the anchor text so you can easily find them. In this case, both links are on the same page. Also, in this instance, the content has been replaced with new content on a different URL. So to fix this, I would need to go to the 'Setting up your first project' page in our CMS, find the two links, and update the href attributes to point to the new page.
All pages in bulk export
From the URL List, click the green button Export Hint Details to generate the Hint export.
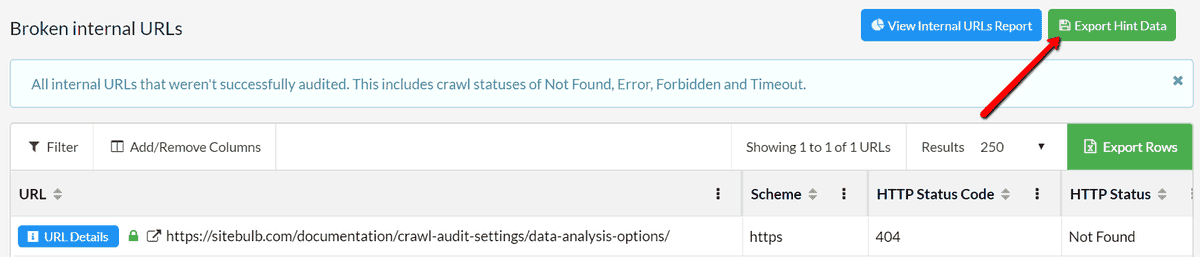
Once this has generated, you can open it directly in Excel, and you will be presented with the data for each broken URL, one per row. Scrolling right will show you other data, until you get to the 'Example Links', which tell you the pages that link back to the broken URL. The export will show 5 example links, which is typically enough to find and fix all links.
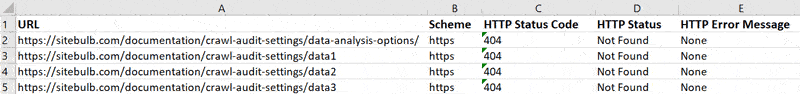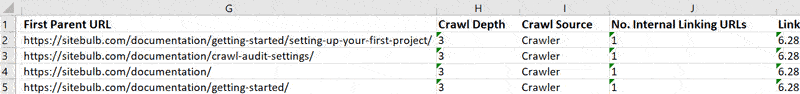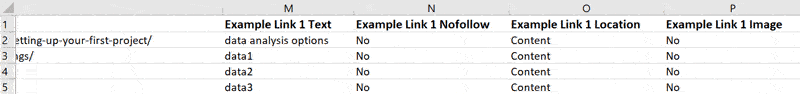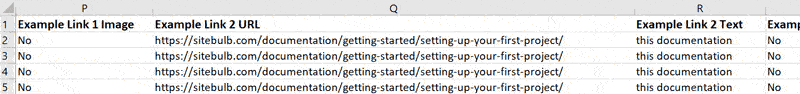
Instances where 5 example links are NOT enough tend to be when the broken link exists in navigation (e.g. broken link in footer) - in which case, fixing the navigation template will allow you to fix all instances of that broken link in one go.
Sitebulb will also help you identify these, look out for these 2 columns:
- No. Internal Linking URLs - this tells you how many pages link to the broken URL. If this number is very high, it is probably a navigation links.
- Example Link 'X' Location - this will either be 'Navigation' or 'Content'. If it is 'Navigation', Sitebulb found the link in one of the navigation areas on the page.
 Sitebulb Desktop
Sitebulb Desktop
Find, fix and communicate technical issues with easy visuals, in-depth insights, & prioritized recommendations across 300+ SEO issues.
- Ideal for SEO professionals, consultants & marketing agencies.
 Sitebulb Cloud
Sitebulb Cloud
Get all the capability of Sitebulb Desktop, accessible via your web browser. Crawl at scale without project, crawl credit, or machine limits.
- Perfect for collaboration, remote teams & extreme scale.
