URLs with similar content
This means that the URL in question has substantially similar HTML content to at least one other indexable URL.
Why is this important?
This could also be referred to as 'near duplicate content', where most of the HTML content on the pages is the same - without the content being identical.
If this sort of duplication occurs, it may be serious issue, as URLs with almost identical content are accessible to search engine crawlers.
If this results in large scale duplicate content issues on the site, you could trip quality algorithms like Google's Panda, which can depress organic search traffic to the site as a whole.
What does the Hint check?
This Hint will trigger for any internal, indexable URL which has big chunks of text content in the <body> that are identical to another indexable URL.
Note: since the duplicate content check is only for indexable URLs, URLs which are canonicalized are not included in the analysis - as the canonical tag 'handles' the duplicate issue.
Examples that trigger this Hint:
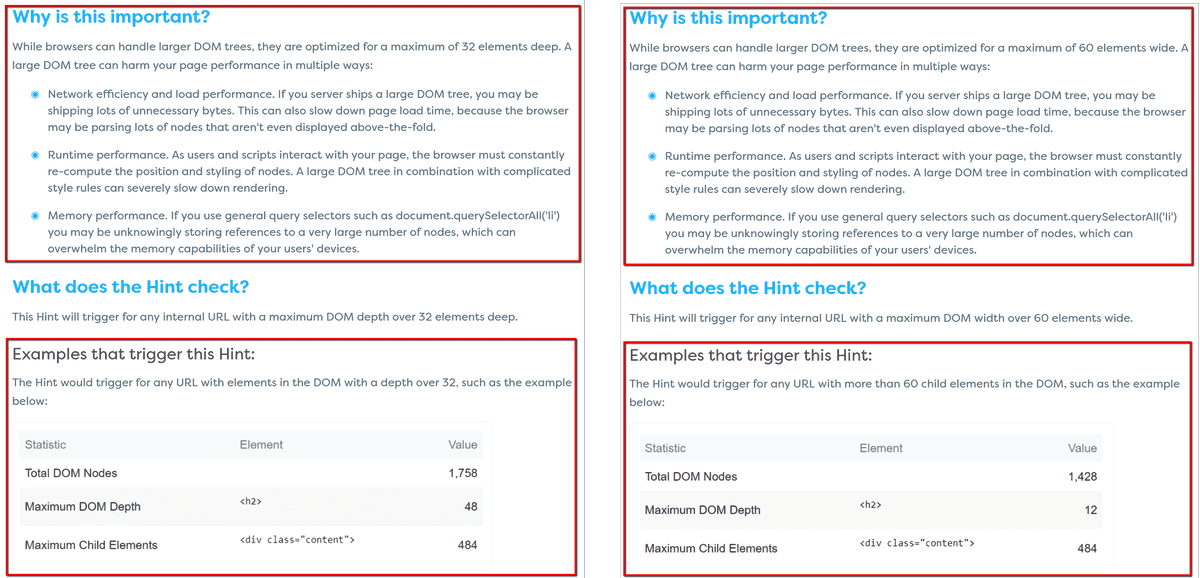
Ironically, some of Sitebulb Hints pages on our website trigger the Hint - when Hints themselves are checking for substantially similar things, the 'Learn More' pages inevitably end up very similar as well. Consider the Hints pages below for 'Avoid excessive DOM depth' and 'Avoid excessive DOM width', these pages trigger the Hint, and you can see from the image below that they have large chunks of content that is exactly the same:
How do you resolve this issue?
As with all duplicate content issues, the seriousness of the issue largely depends on the scale - in general, if only a few pages are affected, it is probably not affecting the site to any meaningful degree. As an example, we are not too worried that a few of our Hints pages have similar content, as the scale is relatively low, and they are not key pages (from a search or conversion perspective) - so we are comfortable with it.
If there are thousands of duplicates, however, the scale might be large enough to trigger a quality algorithm like Panda.
A common source of URLs with duplicate content are landing pages that target very slight variations on the same keyword - with the same text content on the page, but perhaps a different slate of product images. In general, this sort of content is not good for SEO, and search engines will often simply filter it out of search results since the content is too similar. If you do have a content issue like this that you need to resolve, the best way is to create a single unique page that contains enough rich content and crossover keywords that would allow it to rank for a number of related keywords.
Another common situation is if you have the same page content that is deliberately available through multiple paths on the website. An example, on an outdoors ecommerce website, might be that of a pocket torch - where there is a product page accessible via several categories (e.g. Torches, Camping, Travel). The solution for this sort of issue is to select one version of the page to be the canonical (e.g. the Torches one) and add canonical tags to the Camping and Travel versions of the product page. This is exactly the type of issue that canonical tags were designed to solve.
 Sitebulb Desktop
Sitebulb Desktop
Find, fix and communicate technical issues with easy visuals, in-depth insights, & prioritized recommendations across 300+ SEO issues.
- Ideal for SEO professionals, consultants & marketing agencies.
 Sitebulb Cloud
Sitebulb Cloud
Get all the capability of Sitebulb Desktop, accessible via your web browser. Crawl at scale without project, crawl credit, or machine limits.
- Perfect for collaboration, remote teams & extreme scale.