This week, we're pleased to have Julian Mangoka sharing her thoughts on data modeling and its various approaches that can be of benefit to SEO.
In a 2023 Statista global survey, half of the respondents believed that businesses compete on data and analytics, while three-quarters were using data to drive innovation. Big data analytics has become the 'oil' for optimizing the digital domain.
Search engines handle large volumes of data, including datasets related to user behavior and website performance. For example, Google handles more than 20 petabytes of data daily and processes more than 3.5 billion searches per day. And your and your competitors’ website data is among them.
To beat the competition, your SEO strategy should leverage data modeling. Effective data modeling techniques can help you classify, analyze, fragment, and monitor your website data and make data-driven decisions.
This article explores the benefits of data modeling for SEO and provides a step-by-step approach to creating one. Read on to understand how to optimize, measure, and improve the impact of your SEO data model.
Contents:
- What is data modeling for SEO?
- The value of data modeling for SEO
- Understanding the basics of data modeling in SEO
- Types of SEO data models
- Step-by-step guide to creating a data model for SEO
- Examples of SEO data models
- Optimizing your data model for search engines
- Measurement and improvement
What is data modeling for SEO?
Data modeling for SEO involves using tools and strategies to organize, structure, and represent data from a large dataset to understand trends and make SEO-related decisions.
It’s simply transforming raw data into meaningful observations that inform and lead your SEO execution efforts. The dataset may comprise keyword rankings, user behavior, competitor analysis, website traffic, and backlink profiles.
SEO data modeling aims to discover trends and correlations that aren't obvious at a glance, but that significantly impact your SEO efforts and outcomes.
The value of data modeling for SEO
A McKinsey study shows that businesses that have implemented data-driven B2B sales growth engines recorded market and earnings growth of 15-25%. Besides, data modeling helps you understand the data at hand and how it affects your SEO.
Let’s look at the key benefits.
- Guides content optimization: Data modeling helps reveal user preferences, search intent, and pain points, allowing you to tailor content that speaks to your target audiences' demands. For example, analyzing users’ search queries informs your topic choice and keyword clarity for your new content and its optimization.
- Identify and solve technical SEO issues: You can use Google Search Console (GSC) to resolve indexing and crawlability issues and examine load speed and mobile usability. This helps improve your site performance and overall rankings.
- Gain backlink insights: A comprehensive backlink analysis can help you follow their growth trend, spot possible risky connections, and focus on your link profile's overall status.
- Understanding user behavior: Data modeling provides invaluable insights into how users interact with your website, highlighting its friction points. For example, gaining trend data, such as bounce rates, can help you develop data-driven strategies to improve your search engine rankings.
- Monitor Traffic: Traffic data modeling helps you understand the source of your website’s traffic and the impact of organic traffic compared to paid traffic. With this data, you can optimize your website’s visibility on the SERPs.
- Boost competitive edge: SEO data modeling can help you identify and analyze new trends and understand how they impact user intent. Swiftly adapting your strategy to integrate these trends ahead of your rivals is a win.
Understanding the basics of data modeling in SEO
- Schema: An organized data markup that helps search engines create rich snippets such as reviews, ratings, and more. For example, when you mark up an event with schema, you help Google differentiate an event date from an arbitrary date on your page.
- Ontology: Content silos that help arrange and classify content into an understandable structure. Creating content silos based on categories helps search engines track your content relationships. This enhances your website architecture and relevance to particular user queries.
- Entity: These are the main content aspects, such as products, people, or places, and search engines use them to match user queries with the right content. For example, Google's Knowledge Graph depends on entities to provide more relevant search results.
- Attribute: Correlate to particular entity attributes or features and help search engines classify your content better, boosting indexing and visibility. For example, meta tag attributes may include a title and description, and product attributes may include price and color.
- Relationship: Shows how different entities are connected, helping accurately classify data. A practical application is internal linking, where you link related content to indicate a connection to search engines.
Types of SEO data models
Here are the three types of data models that you can use to model and optimize SEO data.
1. Relational data models
Relational data models use tables with rows and columns that define the data and show its relationship at various points.
You can use this model for SEO data like backlink profiles or keyword rankings. For example, you can use different tables for keywords and backlinks and then apply Structured Query Language (SQL) databases to define their relationship. This allows you to study and analyze how your SEO is performing within the two dimensions.
Here’s a visualization of a relational data model applicable to an e-commerce store.
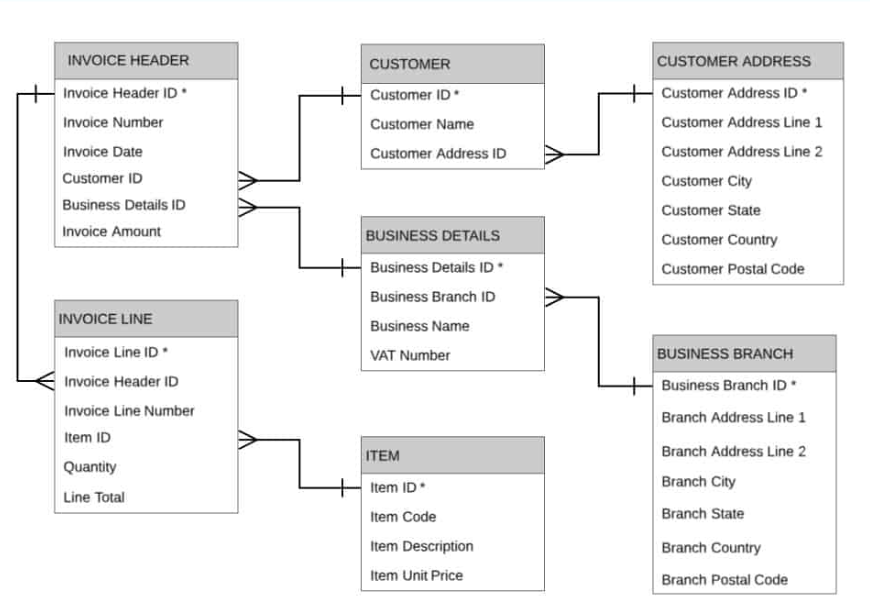
2. Graph data models
Graph data models represent data as entities and show how they are related. For example, you can use a graph model to visualize the relationships between keywords and user behaviors.
You can also study the interrelationship of your pages by analyzing your internal and external link networks, which can help you pinpoint your website’s main authorities.
Here’s a sample graph data model from Sistrix visualizing the relationship between rankings and featured snippets.
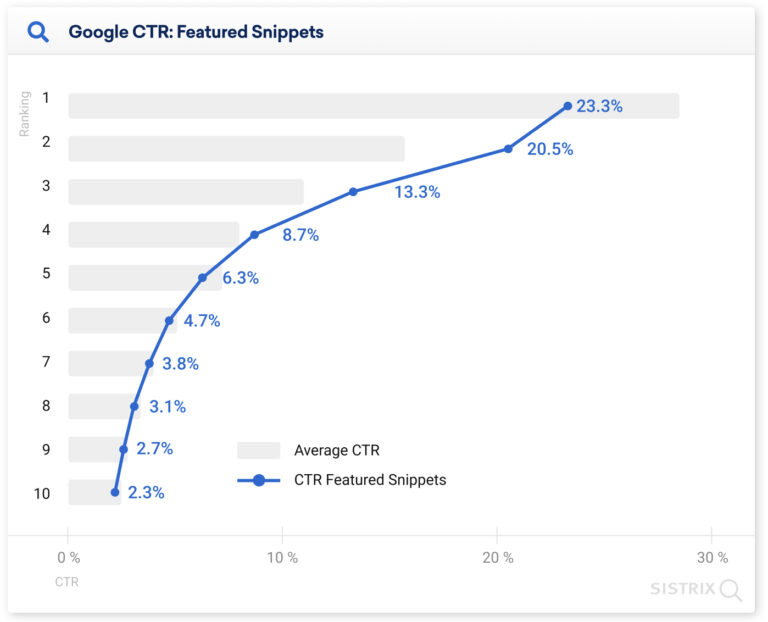
3. Hierarchical data models
Visualize a hierarchical data model as a family tree, where every entity has one parent and perhaps many children. Each data point is connected to another higher point, except the root entity, where the hierarchy starts.
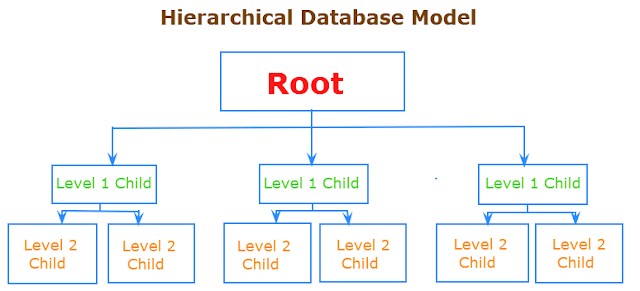
You can use this model to organize your web content into various groups and sub-groups. For example, if you’re doing SEO for an e-commerce website, you can use this model to organize the products into categories, helping search engines crawl and index your content.
A step-by-step guide to creating a data model for SEO
Creating a data model for SEO is a systematic approach, and here’s a step-by-step guide you can apply to create one.
1. Define entities and attributes
Review and outline the main entities for your website structure and their attributes. Here’s a table of the entities to consider and their associated attributes.
Entity |
Attribute |
|
Keyword |
Title, search volume, difficulty, ranking position |
|
Pages |
URL, title, meta description, content, images |
|
Links |
Source, target, anchor text, authority. |
|
SERP |
Search engine, ranking position, featured snippets, competitors. |
|
Traffic |
Organic traffic, clickthrough rate, bounce rate, session duration |
|
Technical SEO |
Load speed, mobile usability, crawlability, indexing |
|
User behavior |
Intent, conversion rate, engagement |
|
Content |
Type, length, quality, freshness. |
2. Establish relationships between entities
For this step, start by mapping the connections and figure out how the entities are connected. Here's how to do that.
- Map keywords to pages: Since each of your pages targets a particular keyword, ensure to map them to their associated keywords based on your optimization strategy.
- Connect pages to links: Track your pages with backlinks and internal links using an organized internal linking strategy.
- Map pages to content: Analyze your content and connect each content piece to its associated page.
- Connect SERP to keywords: Monitor the SERP data and check the impact of keyword rankings on SERP attributes and visibility.
- Link traffic to pages: Link and compare your site traffic data to particular pages and examine how they perform.
- Link technical SEO to pages: Single out technical strands, such as your web load speed, and link them to a specific page to check for any performance issues.
- Connect user behavior to pages: Relate user behavior aspects with your page performance and study the degree of user engagement.
After mapping the connections, generate a visual representation, such as a flowchart, to demonstrate how your entities relate. This gives you a broader view of your data flow and their associations.
Here’s a sample flow chart showing how website aspects can relate:
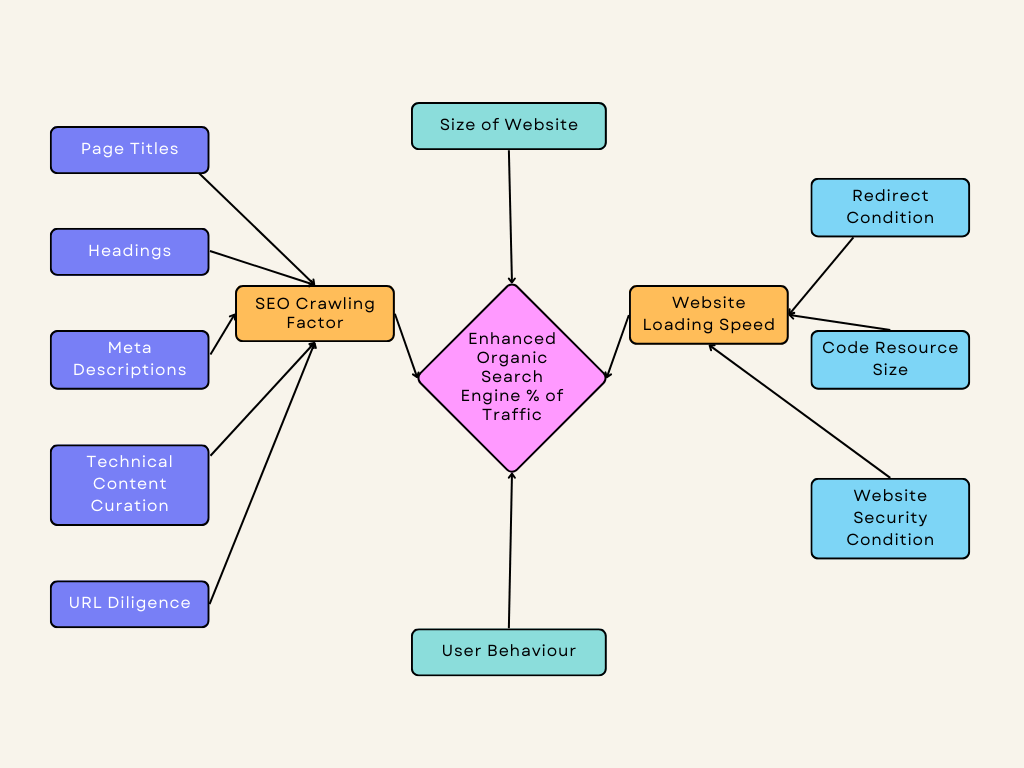
3. Ensure data accuracy and consistency
Here are the processes you can perform to ensure your data is correct and consistent.
- Apply data validation approaches: You can use data validation tools to check for broken links, applicable metadata, and validate schema. You can also regularly do a manual review to examine whether your data is accurate, especially for important attributes, such as titles.
- Carry out periodic audits: Auditing your content often ensures it is always up-to-date and error-free. Ensure you also monitor your keyword rankings and traffic performance.
- Perform consistency checks: Regular checks ensure your data follows a similar format across all entities. For example, you can use a standard layout for all your URLs.
4. Improve visibility with schema markup and SEO tools
Here’s how you can improve SERP visibility:
- Use schema markup: To ensure your data is visible to search engines, you can use schema types for blogs, products, and more. Ensure you embed the schema markup in your page's HTML, or you can use a structured data testing tool like Sitebulb to create and test the markup.
- Use SEO tools: You can use Sitebulb to crawl any website (even JavaScript) and analyze your data quality for any technical concerns, as well as GSC to periodically view your data reports and schema markup issues.
- Track and optimize: Monitor how your implemented schema affects your site's visibility and CTR. Ensure you revamp your schema markup depending on your data metrics and periodic updates.
Examples of SEO data modeling in practice
Data modeling is a strategic process that isn’t very visible from the outside, however we can see some of the outcomes of data modeling. Here are some examples.
1. Amazon
The retail giant uses product schema to help search engines crawl and understand its content.
You'll notice that they have rich snippets displaying their product prices, type, and availability.
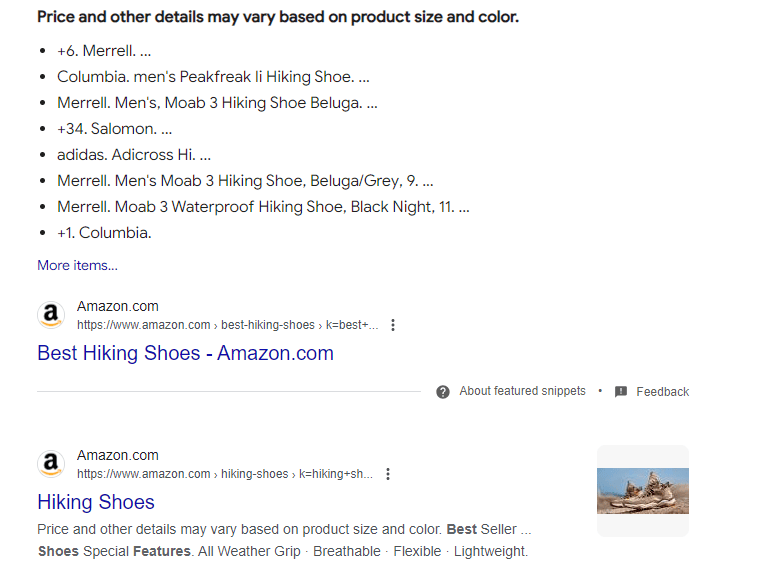
Also, their URLs are keyword-rich, reflecting their product name and group, making it easier to index and rank: /product-category/product-name/
Amazon has a robust internal linking network, linking products to related categories and customer reviews, which spreads link equity across the site.
2. HubSpot
HubSpot organizes its content into categories, such as 'Sales,' 'Marketing,' 'Service,' and more, tagging every article with related topics. This creates topic clusters and gives its content relevance to search engines.
Hubspot also uses schema markup for its articles and includes metadata, such as publication date, author, and article subject, helping to boost CTR.
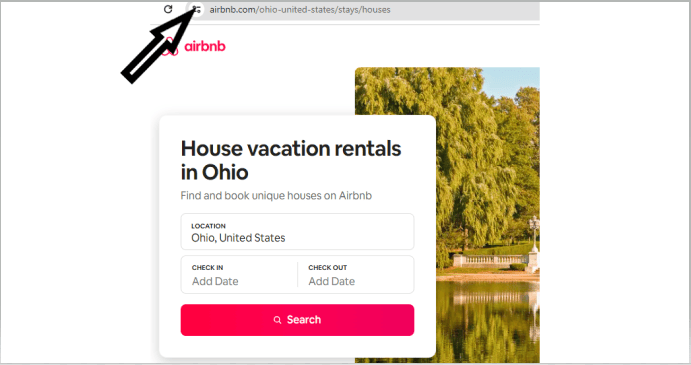
3. Airbnb
Airbnb describes its property listings using structured data like location, property type, availability, and pricing, improving the likelihood of its listings appearing in SERPs.
For example, a search for ‘holiday homes in Ohio’ places Airbnb at position #1 on SERPs.
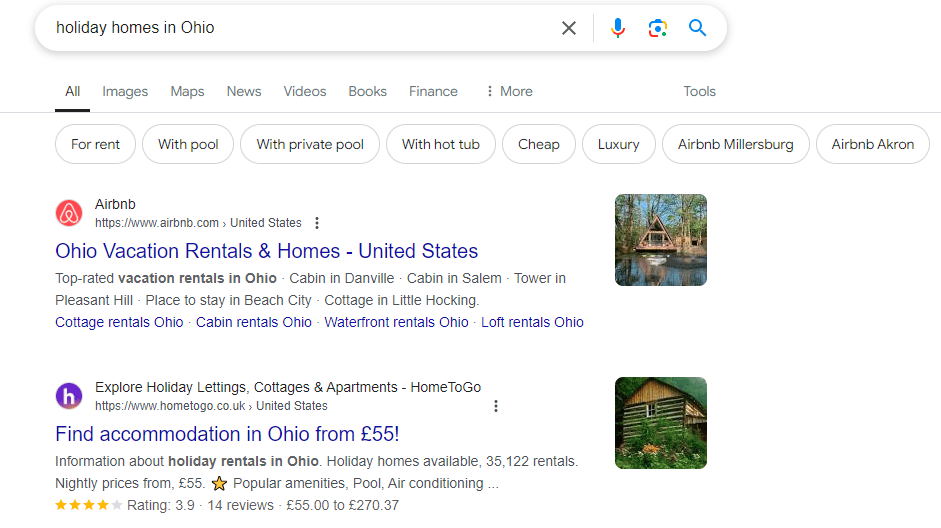
Airbnb also includes user reviews and ratings in its data model, marking it with the right schema to allow search engines to feature them in search results. Airbnb includes property type, city name, and distinctive identifiers in its URLs. An example is /ohio-united-states/stays/houses.
Optimizing your data model for search engines
Optimizing your data model for SEO ensures your metrics correspond to the search engine algorithms, boosting your site indexing and general SEO performance.
Here are some tips for ensuring your data model is optimized for SEO:
1. Use relevant keywords and phrases
Choose relevant primary and secondary keywords and naturally include them in your data attributes. Say you have a website that sells sports shoes, you should strategically use phrases such as "sneakers," "hiking shoes," or "soccer shoes."
Focus on content relevance and user readability. You might also want to avoid keyword cannibalization as Google's John Mueller says it dilutes your content's value.

Also, consider incorporating long-tail keywords that are less competitive and align with the user's intent. For example, rather than using "running shoes," you can use a longer keyword like "best running shoes for the toughest terrain."
2. Structure data effectively
Keep your URLs clean and descriptive, and ensure they mirror your content hierarchy. For example, if one of your pages is "Womens Running Shoes," it may have a URL like /products/womens-running-shoes instead of a strand of arbitrary content.
Sort your data into clear-cut categories that align with user search behavior. If, for example, you operate an e-commerce website, sorting your products by brand, type, and usage helps search engines correctly crawl and index your content.
Also, ensure your data model structure is clear and logical, and visualizes a natural sequence. An example is Category> Subcategory> Product.
3. Use internal linking and cross-referencing
Link your connected entities to enhance UX and for proper search engine indexing. Say you have a blog post on "How to Choose the Right Hiking Shoes," you should link this post to other relevant product pages and associated articles.
However, avoid generic phrases for your internal links anchor text. For example, instead of writing "click here," write specific terms that align with your target content, like "explore our variety of trail running shoes."
Remember to apply breadcrumb navigation to enhance user navigation and strengthen your site structure for search engines.
Measurement and improvement
It’s not just enough to implement your data model. You should continuously monitor your website performance metrics to stay ahead of the competition.
Monitoring SEO performance
You can use analytics tools to track your SEO performance. Some relevant tools are:
- Google Analytics (GA): You can use GA to monitor different SEO metrics, like conversion rates, organic traffic, and user behavior. The tool allows you to apply custom reports to track metrics like bounce rate, pages per session, and average user duration per session.
- Google Search Console: This tool can help you monitor your pages’ indexing rate and review crawl errors. This way, you understand how your model impacts your search engine rankings and site visibility.
- Sitebulb: Sitebulb is a website auditing tool that allows you to do an in-depth technical website audit. It can analyze your site's internal linking, overall structure, load speed, schema, hreflang, and more.
Making iterative improvements
Depending on your SEO feedback and performance metrics, ensure you refine your model. Here's how you can do it:
- Update your schema markup: Continuously expand your schema markup depending on your content performance on SERPs. If you realize your rich snippets aren't showing, examine your schema markup for errors or areas to add extra details, and ensure you’re optimizing for different featured snippets.
- Optimize your keywords: Periodically update your keywords by revisiting your category names or metadata to ensure they align with new search trends and updates.
- Modify your internal links: Adjust your internal links accordingly, depending on your site's performance and user behavior. For example, if some of your pages are underperforming, link them from your higher-traffic pages to increase their visibility. Also, frequently audit your internal links for relevance and effectiveness.
- Keep track of algorithm updates: Ensure you are always informed about major algorithm updates and how they may affect your site. Adapt and adjust your data model appropriately to match the new best practices.
Conclusion
Data modeling for SEO is an important strategy you can't afford to ignore if you want to organize your website content and improve visibility. By effectively using suitable keywords, internal linking, and implementing logical data flow, a strategically optimized data model helps Google understand your content and rank it better. So, incorporating data modeling into your SEO strategy is a great way to boost your website traffic and ranking position.
You might also like:
Sitebulb is a proud partner of Women in Tech SEO! This author is part of the WTS community. Discover all our Women in Tech SEO articles.

Julian is a seasoned content writer specializing in B2B SaaS and Fintech. She is passionate about crafting premium, SEO-optimized content that helps businesses achieve growth and visibility. Outside of work, Julian enjoys exploring the great outdoors through hiking adventures.
Articles for every stage in your SEO journey. Jump on board.
Related Articles
 Why Your SEO Strategy Still Matters for AI Search (And What Needs to Change)
Why Your SEO Strategy Still Matters for AI Search (And What Needs to Change)
 Beyond the Basics: How to Turn Crawl Data Into Strategic Actionable SEO Insights
Beyond the Basics: How to Turn Crawl Data Into Strategic Actionable SEO Insights
 Spam-Free Reddit for SEO Webinar: Visibility, Reputation, Community
Spam-Free Reddit for SEO Webinar: Visibility, Reputation, Community
 Sitebulb Desktop
Sitebulb Desktop
Find, fix and communicate technical issues with easy visuals, in-depth insights, & prioritized recommendations across 300+ SEO issues.
- Ideal for SEO professionals, consultants & marketing agencies.
Try our fully featured 14 day trial. No credit card required.
Try Sitebulb for free Sitebulb Cloud
Sitebulb Cloud
Get all the capability of Sitebulb Desktop, accessible via your web browser. Crawl at scale without project, crawl credit, or machine limits.
- Perfect for collaboration, remote teams & extreme scale.
If you’re using another cloud crawler, you will definitely save money with Sitebulb.
Explore Sitebulb Cloud


 Julian Mangoka
Julian Mangoka

