How to Audit Crawl Depth & Improve Crawl Efficiency
Published January 27, 2025
This week, it’s a warm welcome and big thank you to Bengu Sarica Dincer for her insights into auditing crawl depth and improving crawl efficiency.
When I first began my professional career in SEO, the search engine results pages (SERPs) I encountered were completely different from what we see today. In fact, I could say there are very few similarities.
The biggest reason for this, of course, is the massive increase in the amount of indexed content. And now, AI-generated content has joined the scene as well. This means that it is now more challenging than ever to get all of a website's pages indexed and ranked well.
Plus, alongside the traditional use of search engines, searching through LLMs (large language models) has become an integral part of our lives—even though they aren't technically search engines for now. This means that websites now need to be compatible with LLM-powered chatbots (or answer engines) like Gemini, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, etc. In simpler terms, focusing on improving your website's crawl efficiency has become more important than ever before.
So if you want to ensure that your web pages are being crawled by search engines and answer engines, keep reading. In this article, we’ll explore various strategies for auditing your website's crawl depth and discuss different tactics to enhance crawl efficiency. I have focused on uncommon information in this article, since you probably already know things like giving importance to internal link structure, speeding up the website, fixing broken links, etc.
Contents:
- Why crawl depth isn’t just a technical metric
- How crawl depth impacts crawl equity
- Best practices for auditing crawl depth
- Tactics for improving crawl efficiency
- How to measure success for crawl depth
- Common mistakes to avoid
Why crawl depth isn’t just a technical metric
I have to admit that I assumed crawl depth as nothing more than a technical and straightforward metric when I first started working in technical SEO. But as I got to work on it – and as bad experiences taught me valuable lessons – I realized that this metric holds significance beyond its technical context. Let me explain how.
As you already know, crawl depth refers to the distance between any starting page and a specific page, measured by the number of clicks it takes to reach that page.
So, from a technical point of view, low crawl depth facilitates an optimized website architecture. But this also means having a user-friendly, easy-to-navigate website that doesn’t test the patience of visitors. Win win.
In short, simplicity is key. The shorter the distance between web pages, the faster crawl efficiency tends to be and the better user experience.
And I’m not the only one who thinks this metric is worth noting. Search engines and LLM-powered answer engines share this perspective. Now, let’s discuss how search engines allocate their crawl resources across your website, aka crawl equity.
How crawl depth impacts crawl equity
I see crawl equity as an invisible hand guiding crawler behaviour. Because crawl equity determines how search engine crawlers allocate their attention across your pages. The logic is simple: we want crawlers to focus their limited resources on our most critical pages.
But what does this actually mean?
Crawl equity is synonymous with page importance. Pages with high crawl equity are considered as more valuable and, as a result, are crawled more frequently and deeper, so ultimately increasing their chances of ranking well in search results.
Just think! Crawlers have limited resources and time, much like users browsing a website. They tend to stick closer to easily accessible, surface-level content that’s simple to navigate and understand. Pages buried deep within your site’s structure often end up overlooked, with lower crawl equity as a result.
So, if your most important pages are hidden deep within your site by being buried under layers of links or lost in complex navigation, they’re at a disadvantage. They’ll get indexed slower, be less visible and ultimately receive a hit to their organic traffic.
Best practices for auditing crawl depth
SEO tools like Sitebulb are invaluable for this process. However, applying additional methods may provide a more indepth understanding of page depth and user behaviour. I mean, combining different methods can offer the full picture about your website structure.
Exploring the complexities of crawl depth can feel both challenging and rewarding. Over time, I’ve developed a set of strategies for auditing crawl depth. Let’s explore these approaches and build a solid foundation for SEO strategies that improve crawl efficiency.
1. Benefit from heatmaps and session recordings
Understanding your audience's behaviour can really help you improve your site architecture, ultimately helping to improve crawl efficiency. At this point, heatmaps and session recordings come into play.
Heatmaps provide a clear, visual snapshot of user interactions across your website. Session recordings, on the other hand, act like a virtual playback, letting you watch how users move through your site in real-time. There are many tools that you can use like Microsoft Clarity which is a free tool, Hotjar, PostHog and other options to analyze user behaviours.
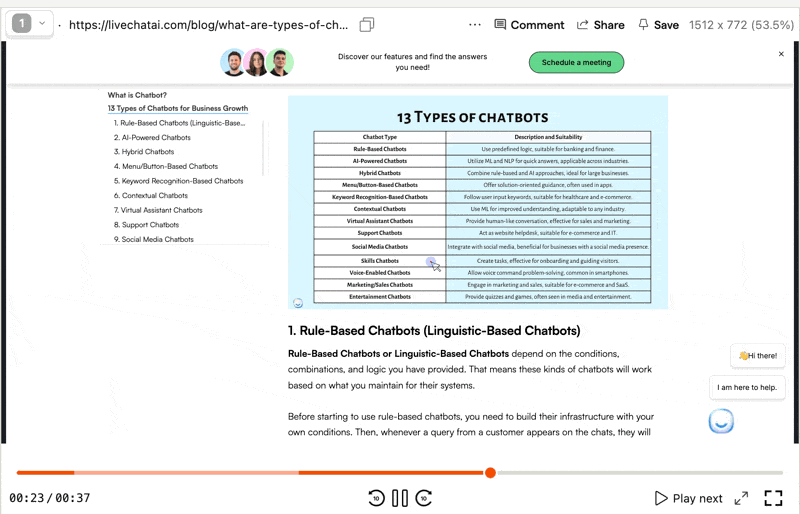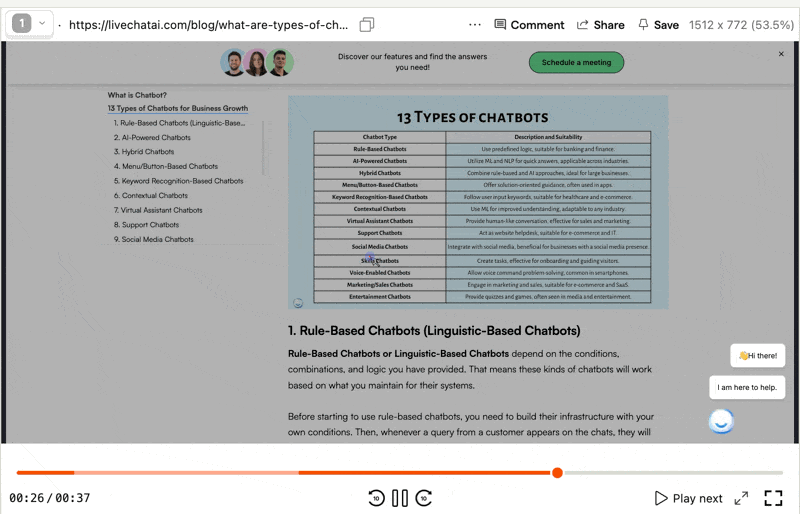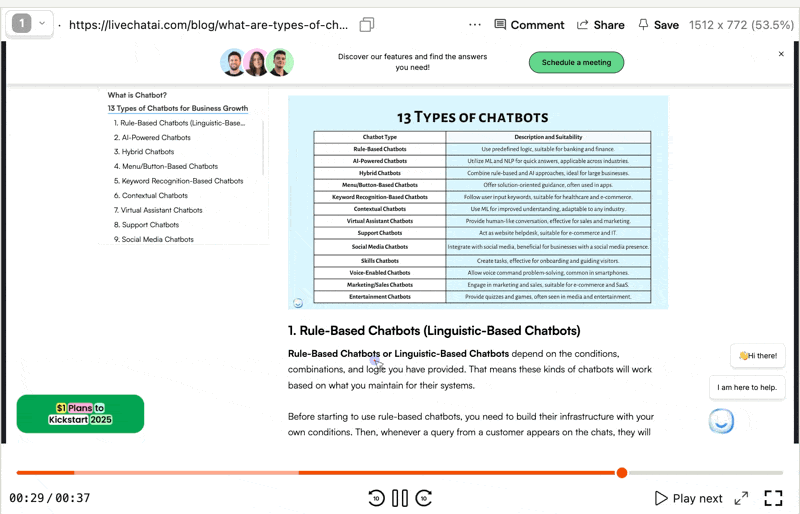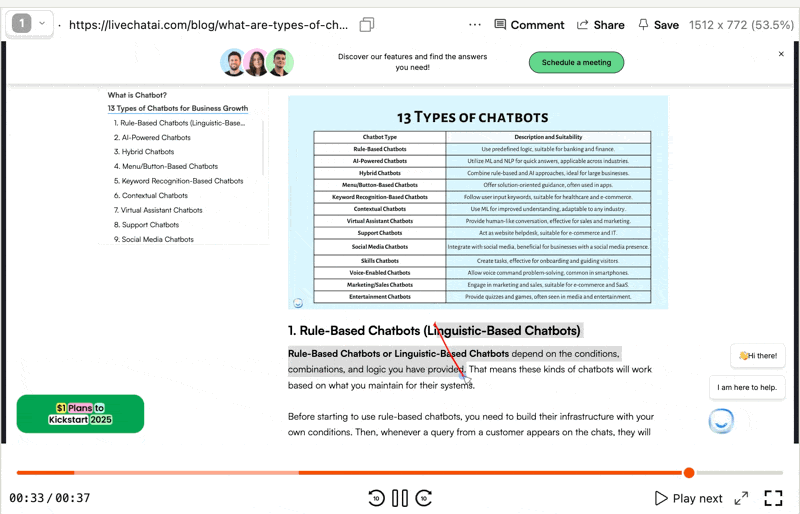
An example to a screen recording session
Track the user's journey from the homepage or other significant landing pages. How many clicks do they make before they hit their final destination? This number should ideally match your target crawl depth.
Observe if users follow the intended site architecture or get off the track in undesired directions. Align their practical journey with your architectural vision.
Spotting high exit points are my favourite parts. If users are abandoning a page you’ve designed as a midway point, you better look at a high crawl depth negative indicator. If users are struggling, chances are crawlers are too.
2. Use version control to compare historical sitemaps
Version comparisons might sound primitive, but they can provide invaluable insights that are often disregarded.
If we see a sitemap of a website as a treasure map for crawlers, then what can be better than comparing previous sitemaps against your current one to understand the evolution and efficiency of your site structure?
You need to use version control systems to store historical sitemaps. If you already use it, then you can spot trends in your site structure's evolution. Were there times when your crawl depth was low and conversions were soaring? Get benefit from these golden periods to enjoy success once again.
Do you notice pages that once enjoyed a low crawl depth and high visibility but are now lost in the depths? Make them in the spotlight again by optimizing and improving.
3. Visualize depth and internal link flow
Visualization of your internal link structure can help you identify issues with crawl depth and overall site structure, allowing for an efficient auditing process.
Seeing is believing, isn't it? By visualizing your website's depth and internal link flow, you can instantly spot irregularities, bottlenecks, and opportunities to streamline.
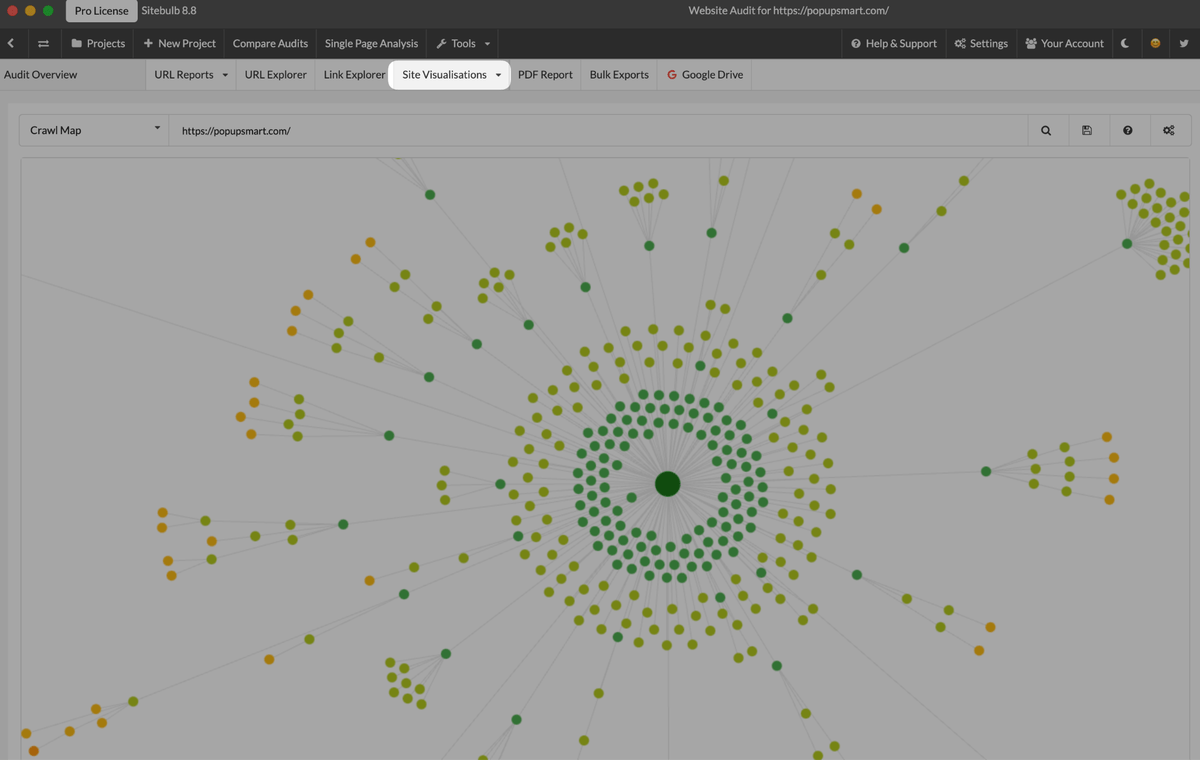
Sitebulb can help you map this out easily. The only thing you need to do is choose the most useful site visualization method from crawl map, crawl tree, crawl radial, directory map, directory tree, and directory radial, from the upper bar in the audit overview. Crawl map is my favourite one as you can understand from the example I've shared above.
4. Build predictive insights with AI
We're living through exciting technological times, right? With AI becoming more common in our daily lives, it’s amazing how it lets us do things we once thought impossible. So, why not use AI to help with auditing crawl depth?
For this, export the log files from the website management platform you use. Then, import these raw files into ChatGPT or another LLM platform you use and enter a prompt to ask the platform to parse the data and analyze which pages are consuming the most crawl resources.
To take the analysis even further, you can export backlink profile data from Ahrefs or another SEO tool that allows you to track backlinks and import it into ChatGPT. Then write a prompt to identify pages with strong backlink profiles but high crawl depth. This allows you to audit pages that should be prioritized for crawlability but are currently overlooked, giving you valuable insights into which pages to focus on.
You can use this prompt that I have already tested but you may need to tweak it a bit according to your expectations and file formats:
Identify and analyze pages with strong backlink profiles but high crawl depth from log files.
Context
Websites with strong backlink profiles are often valuable for SEO. However, pages with high crawl depth might not be easily accessible to search engine bots, potentially affecting their ranking and visibility. Analyzing log files can help in identifying such pages, providing insights for improving their accessibility and overall SEO performance.
Requirements
- Parse the provided log file on crawl data and extract information from the imported backlink data
- Identify pages that have high backlink profiles but also possess high crawl depth.
- Provide insights on improving the crawl depth of these pages to enhance their SEO performance.
Output Format
- A summary table listing pages with strong backlink profiles and high crawl depth.
- Detailed analysis and insights on each identified page.
- Recommendations for reducing crawl depth for the identified pages.
Additional Instructions
- Focus on accuracy in parsing the log files.
- Ensure that the analysis is actionable and provides clear steps for improvement.
- Maintain clarity and conciseness in presenting the findings.
Input Fields:
- LogFiles: Provide the path or location of the log files to be analyzed.
- Backlink data: Provide the backlink numbers of URLS to be analyzed.
As an illustration, you can see ChatGPT’s response with a crawl analysis example.
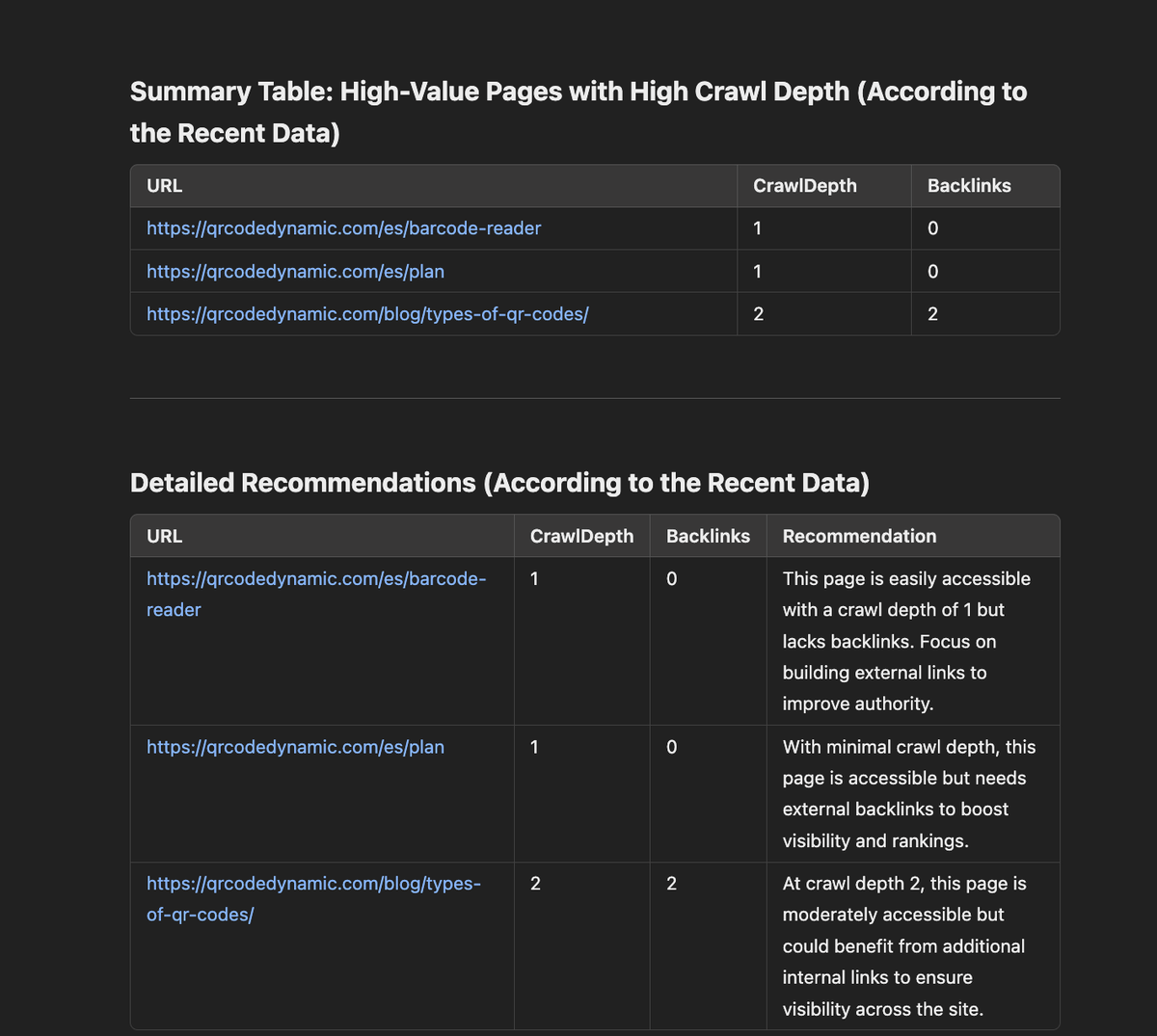
What’s even better is that by using these AI platforms not just once but continuously, we can compare past and current data, and train the system to predict crawl priorities more effectively based on daily files.
💡 On this point, I must say one thing too. Over-reliance on AI for SEO audit strategies can lead to vital mistakes. Always complement it with your practical insights for a balanced auditing strategy.
Tactics for improving crawl efficiency
With the knowledge of different strategies to audit crawl depth, now let's discover the next big question: how to improve crawl efficiency? For many SEOs, this is where the real challenge begins.
Think of your website like a city’s public transit system. When your trains (or web pages) run smoothly, taking users (and crawlers) quickly and easily to their destinations (your content or conversion goals), everything works perfectly. But if the system is plagued by delays, breakdowns, or poorly planned routes, the entire city (your website) starts to struggle.
Keeping that analogy in mind, let’s see some practical tactics to get your site running like a well-oiled machine and improve its crawl efficiency.
1. Test how crawlers render JavaScript-heavy content
As the web has been more interactive, JavaScript has become a key player in creating dynamic and engaging websites. But not all search engines handle JavaScript-heavy content equally well.
The first step in improving crawl efficiency is making sure your content is easily accessible to crawlers, no matter what coding language you use. That’s why it’s so important to inspect and test JavaScript-loaded elements regularly to ensure your crawl pathways remain clear and problem-free.
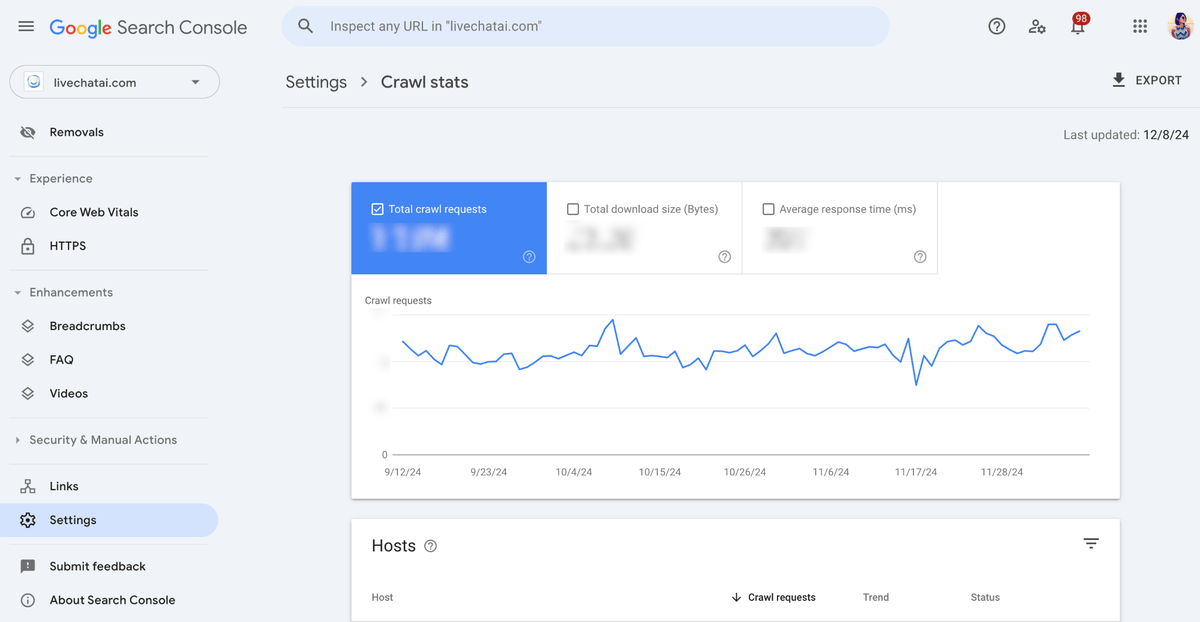
To do this, you can use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to quickly check how bots view and process your pages. Bing Webmaster Tools also offers a similar feature to identify any rendering issues affecting your site.
Alternatively, tools like Sitebulb can help you audit JavaScript-heavy websites by comparing rendered HTML with the raw response HTML. This makes it easier to spot whether your JavaScript elements are slowing down the crawl process so you can fine-tune them and create a smoother experience for crawlers.
Editor’s Note: We’ve created a hub of information on JavaScript SEO and produced a free on-demand JavaScript SEO training course to help you get ahead of the JS curve!
2. Use meta tags dynamically based on business priorities or seasonal trends
To increase crawl efficiency, I highly recommend setting meta directives like noindex to prevent seasonal or campaign-related content from being indexed during off-season or campaign end periods. By doing this, you prioritize more important content for crawling.
For example, during major sales events or holiday campaigns, you can prioritize landing pages or high-performing product pages by allowing them to be indexed. However, once the campaign or season is over, there’s no point in crawling them because you don’t expect any conversion through them.
3. Simplify rendered content for crawlers
As we all know, bots can’t see images or watch videos like we do. Instead, they rely on alt texts, file names, and similar elements to understand the content. This means it’s crucial to keep your website’s content simple and easy for crawlers to understand.
So avoid unnecessary complexities in your site's background to ensure that crawlers can do their job efficiently. However, if you must include more complex elements, you can adopt hybrid rendering. By combining server-side and client-side rendering based on the crawler type, you may improve indexing efficiency without compromising the user experience.
Hybrid rendering works by rendering the core content of a page on the server, delivering it directly to both browsers and search engines. This ensures that both crawlers and users can quickly access the main content and markup.
While this approach provides faster content and link discovery for search engines and ensures a quicker content delivery to users, it also has challenges. Implementing hybrid rendering can be complex. Additionally, the need for dual rendering on both the server and client side can cause performance issues if not managed carefully.
At the end of the day, simpler is always better. So consider providing simplified content for crawlers to get the best results.
How to measure success for crawl depth
This process is not just a one-way street focused on numbers and metrics. Real success is seeing the impact of your optimization on goals: Higher crawl efficiency, improved user experience, better search rankings, eventually all leading to your desired marketing goals.
Yet, to understand the root of crawl depth success, it is better to watch some metrics like the ones below before and after the applied optimizations:
Crawl efficiency ratio: To find this, compare the number of crawled pages vs. indexed pages over time. A higher ratio suggests improved efficiency.
Time-to-index: You can find it by measuring how quickly new or updated content gets indexed. Faster indexing indicates better crawl depth management.
Depth distribution: Some SEO tools can analyze whether critical pages are within 3-4 clicks of the homepage.
After observing those metrics, you should analyze to find if they make sense or not. Has there been a notable change? Do you achieve shorter crawl depth, healthier URL rating, and more internal links?
Additionally, Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools are handy ones for getting insights from search engines. They provide crawl stats showing how often bots crawl your website and the number of URL crawled per day. These sections are treasure troves to measure crawl depth success.
Common mistakes to avoid
SEOs sometimes experience these common mistakes during our crawl depth efforts. Learning from these missteps can save you time, effort, and significantly help to improve crawl efficiency. Let's run through each of these pitfalls, understanding why they happen and how to avoid them.
Over-optimizing for crawl budget
In theory, streamlining your website’s architecture to allow search engine crawlers easy access to all of your pages sounds like a plan. After all, isn't it great if crawlers can reach your lowest depth pages with the fewest hops? Yes, but like all things in life, balance matters in optimization as well!
Over-optimizing can lead to a situation where too many links are placed on a single page, causing potential keyword cannibalization (where several pages compete for the same keywords). In this type of situation, crawlers might get overwhelmed by the massive amount of links, decreasing the value of each one.
To find the balance, be mindful of the number and relevance of the links on your pages. Make every internal link count! This will ensure that your low depth pages get indexed without overwhelming crawlers or cannibalizing your own keywords.
Setting random crawl depth goals
The allure of hitting an ‘eye of the tiger’ crawl depth of 3 for all pages is a goal that might blind you. Setting these targets irrationally, without backing them with concrete data and context, can lead you to anything but a success.
Sure, maintaining a low crawl depth could be ideal in most cases, but it's not generic. Your website's unique characteristics, such as size, complexity, niche, content distribution, among others, play a significant role in defining this “ideal” crawl depth for your website.
Only focusing on Google and ignoring others
We SEO folks tend to view everything from Google’s perspective. I’ll admit, I’ve been guilty of it too. Its global search engine market share affects us, for sure. But that’s where we trip up!
While optimizing for Google, we often forget about other search engines like Bing, Yahoo, or DuckDuckGo, even SearchGPT and LLM-powered answer engines. Each of these has their own crawl algorithms and customer segments and we might be missing out on those leads by only focusing on Google.
So I strongly recommend you not to ignore other search engines while optimizing your crawl depth strategy. Expand your scope to cover the differences of various search engines and answer engines.
Conclusion
I hope these insights, anecdotes, and tips are useful for you. Good luck with your user satisfaction, positive rankings, and desired conversions!
You might also like:
Sitebulb is a proud partner of Women in Tech SEO! This author is part of the WTS community. Discover all our Women in Tech SEO articles.

Bengu Sarica Dincer currently works as SEO Manager at Designmodo. She consistently seeks innovative strategies to enhance website performance, increase organic rankings, improve user experience, and maximize conversion rates. She loves publishing articles and participating in events as a speaker or attendee and meeting new people at every opportunity.
Articles for every stage in your SEO journey. Jump on board.
Related Articles
 JavaScript SEO AMA with Sam Torres: 13 Questions & Answers
JavaScript SEO AMA with Sam Torres: 13 Questions & Answers
 These WordPress Website Mistakes Could Hurt Your Brand’s Credibility
These WordPress Website Mistakes Could Hurt Your Brand’s Credibility
 Advanced SEO Guide to Rendering: How to Debug, Test & Control What Google Sees
Advanced SEO Guide to Rendering: How to Debug, Test & Control What Google Sees
 Sitebulb Desktop
Sitebulb Desktop
Find, fix and communicate technical issues with easy visuals, in-depth insights, & prioritized recommendations across 300+ SEO issues.
- Ideal for SEO professionals, consultants & marketing agencies.
Try our fully featured 14 day trial. No credit card required.
Try Sitebulb for free Sitebulb Cloud
Sitebulb Cloud
Get all the capability of Sitebulb Desktop, accessible via your web browser. Crawl at scale without project, crawl credit, or machine limits.
- Perfect for collaboration, remote teams & extreme scale.
If you’re using another cloud crawler, you will definitely save money with Sitebulb.
Explore Sitebulb Cloud Bengu Sarica Dincer
Bengu Sarica Dincer